What are Probiotics?
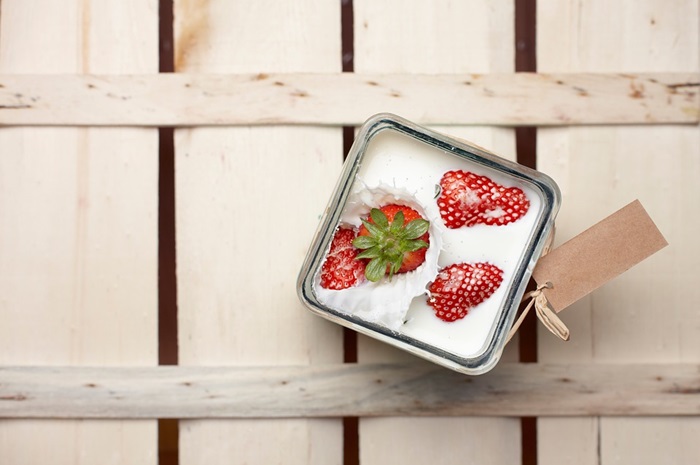
Probiotics are live microorganisms, most commonly bacteria and yeasts, that offer health benefits when consumed or applied to the body. These "good" microbes play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy gut microbiome, the vast community of microorganisms residing in our digestive system. The gut microbiome plays a vital role in digestion, nutrient absorption, immune function, and even mental health.
While some bacteria can cause illness, probiotics are the beneficial kind that help keep our gut in balance. They work by:
- Crowding out bad bacteria: Probiotics compete with harmful bacteria for space and resources, preventing them from colonizing the gut and causing problems.
- Producing beneficial substances: Probiotics produce lactic acid and other substances that can inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria and promote the growth of other beneficial bacteria.
- Stimulating the immune system: Probiotics can interact with the immune system cells in the gut, helping to regulate inflammation and protect against infections.
Sources of Probiotics
Probiotics can be found in two main sources:
1. Food:
- Fermented foods: These are foods that have undergone a natural fermentation process by bacteria and yeasts. Examples include yogurt, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, miso, tempeh, and kombucha. These foods are rich in specific probiotic strains, like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium.
- Some cheeses: Certain cheeses, particularly aged varieties, may also contain live probiotics.
2. Supplements:
Probiotic supplements are available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, powders, and even chewable gummies. These supplements can contain a single strain of bacteria or a combination of strains.
Benefits of Probiotics
Research on the health benefits of probiotics is ongoing, but they have been shown to be helpful for various conditions, including:
- Diarrhea: Probiotics can help shorten the duration of diarrhea caused by antibiotics, rotavirus, and traveler's diarrhea.
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): Probiotics may help to alleviate symptoms of IBS, such as bloating, gas, pain, and constipation.
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Probiotics may help to reduce inflammation and maintain remission in people with ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease.
- Eczema and allergies: Probiotics may help to prevent eczema and allergies in infants and children.
- Immune function: Probiotics may help to boost the immune system and reduce the risk of upper respiratory infections.
Japanese Probiotics
Japan has a long history of consuming fermented foods rich in probiotics. Some notable examples of Japanese probiotics include:
- Natto: A traditional Japanese food made from fermented soybeans. Natto is known for its strong flavor and slimy texture and contains a specific probiotic strain called Bacillus subtilis. Studies suggest natto may help lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- Amazake: A sweet, non-alcoholic beverage made from fermented rice. Amazake is a good source of probiotics and prebiotics (fibers that feed good bacteria) and is often consumed as a breakfast drink or ingredient in desserts.
- Miso: A fermented soybean paste used as a base for miso soup and a variety of other dishes. Miso is rich in various probiotic strains and offers numerous health benefits, including improved digestion and immune function.
Choosing the Right Probiotics for You
With the vast array of probiotic options available, choosing the right one can be overwhelming. Here are some factors to consider:
- The specific health condition you want to address: Different probiotic strains may offer different health benefits. Talk to your doctor about which strain might be most suitable for your needs.
- Dosage: The recommended dosage of probiotics can vary depending on the product and the specific health condition being addressed.
- Form: Probiotics come in various forms, so choose one that you are comfortable taking regularly.
- Safety: Probiotics are generally safe for most healthy adults. However, people with compromised immune systems or those taking certain medications should consult their doctor before starting probiotics.
It's important to note that the research on probiotics is ongoing, and not all strains have proven health benefits. Always choose a reputable brand and consult your doctor before taking any new supplements, including probiotics.