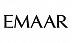IBM REPORT: SAUDI ARABIA CONTINUES TO BE TARGETED BY CYBER THREAT ACTORS
Saudi Arabian organizations are increasingly targeted by threats such as deployment of backdoors, spam campaigns, ransomware and adware
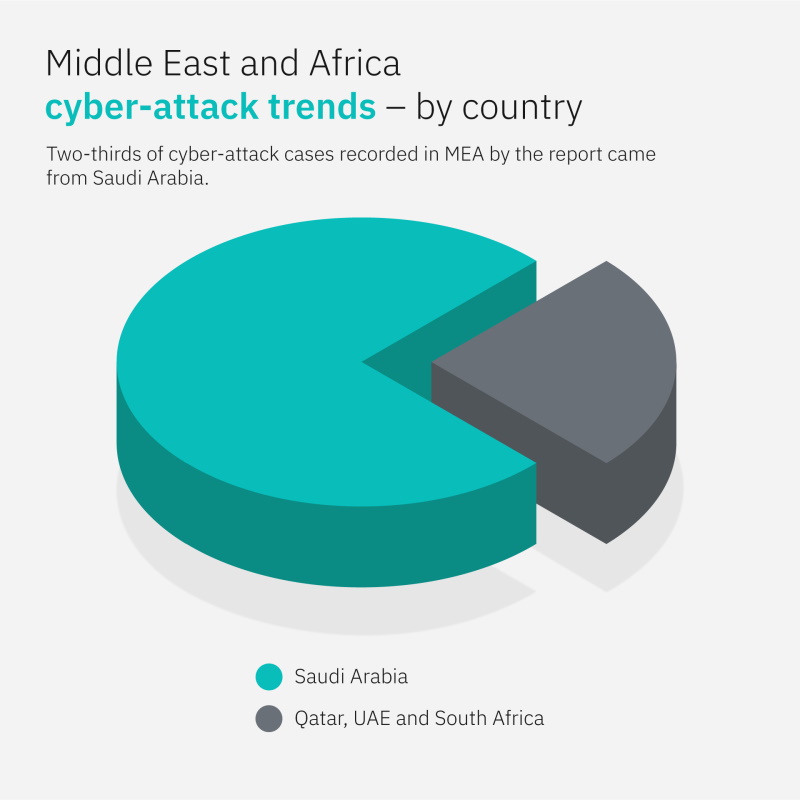
With threat actors finding new and innovative ways to launch cyberattacks, Saudi Arabia remains one of the most targeted countries in the Middle East and Africa (MEA) region, accounting for two-thirds of the cases according to IBM Security’s annual X-Force Threat Intelligence Index.
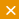
The 2023 report highlights that at 40% the deployment of backdoors was the most common attacker action in cases X-Force responded to in Saudi Arabia. Other actions observed range from spam campaigns to ransomware and adware.
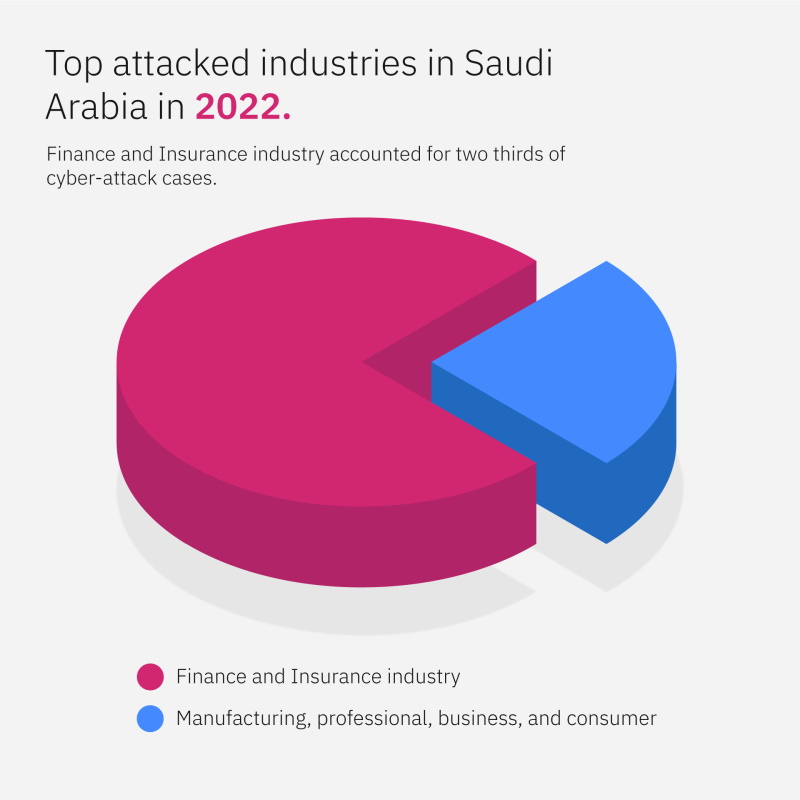
As per the index, finance and insurance organizations accounted for two-thirds of cases, with the remainder split between manufacturing and professional, business, and consumer services.
The report ranks the Middle East and Africa fifth on its list of regions with the highest share of cyber-attacks observed by X-Force, accounting for 4% in 2022, which was down from 14% in 2021. Asia Pacific was named as the most targeted region, accounting for 31% of attacks identified globally. Europe placed second — accounting for 28% of attacks —North America third with 25%, and Latin America fourth with 12%.
“Saudi Arabia, as with much of the region, is undergoing tremendous digital transformation. With the Kingdom now recognized as one of the most connected countries in the world, proactive action must be taken to prevent and hinder cyberattacks”, said Fahad AlAnazi, General Manager, IBM Saudi Arabia. “This is essential to safeguarding the nation’s interests, growth, and development. By being systematic in approach and exercising foresight, we can futureproof the Kingdom, improving security and averting potential crises.”
AlAnazi continued: “IBM Security provides enterprise cybersecurity solutions to help businesses thrive in the face of uncertainty. As the largest enterprise security provider, we have developed an advanced and integrated portfolio of enterprise security products and services. These offerings — ranging from our ransomware protection to cloud security solutions — are powered by AI and a modern approach to security strategy using zero trust principles. Equipping our clients with these tools, we empower the entities that we support to effectively manage and govern risk.”
Globally, the X-Force Threat Intelligence Index finds that although ransomware’s share of incidents declined only slightly (4 percentage points) in 2022, defenders were more successful in detecting and preventing ransomware. Despite this, attackers continued to innovate, with the report showing the average time to complete a ransomware attack dropped from two months down to less than four days.
The IBM Security X-Force Threat Intelligence Index tracks the new and existing trends and attack patterns — pulling from billions of data points from network and endpoint devices, incident response engagements, and other sources.
Some of the key findings in the 2023 report include:
- Extortion: Threat Actors Go-to Method. The most common impact from cyberattacks in 2022 was extortion, which was primarily achieved through ransomware or business email compromise attacks. Europe was the most targeted region for this method, representing 44% of extortion cases observed, as threat actors sought to exploit geopolitical tensions.
- Cybercriminals Weaponize Email Conversations. Thread hijacking saw a significant rise in 2022, with attackers using compromised email accounts to reply within ongoing conversations posing as the original participant. X-Force observed the rate of monthly attempts increase by 100% compared to 2021 data.
- Legacy Exploits Still Doing the Job. The proportion of known exploits relative to vulnerabilities declined 10 percentage points from 2018 to 2022, due to the fact that the number of vulnerabilities hit another all-time high. The findings indicate that legacy exploits enabled older malware infections such as WannaCry and Conficker to continue to exist and spread.