Cisco Midyear Security Report Reveals Cyberattacks Are Becoming Even More Sophisticated
The Cisco® 2015 Midyear Security Report released today, which analyzes threat intelligence and cybersecurity trends, reveals the critical need for organizations to reduce time to detection (TTD) in order to remediate against sophisticated attacks by highly motivated threat actors.
The report covers two main areas:
Threat Intelligence
This section gives an overview of the latest threat research from Cisco and discusses:
Criminals’ increasing use of macros involving Microsoft Office
New tactics from malware authors to evade detection
Risk of malware encounters for specific industry verticals
Time to detection of threats
Updates on spam, threat alerts, Java exploits, and malvertising
Analysis and Observations
This section focusses on security industry consolidation and the emerging concept of integrated threat defense. Other topics in focus include the importance of building trust and security into products and the value of engaging security services organizations in a market where skilled security talent is scarce. The report discusses how a cohesive cyber-governance framework can be a step toward sustaining business innovation and economic growth on the global stage.
Key Highlights for the 2015 Midyear Report:
Adversaries continue to innovate as they slip into networks undetected and evade security measures.
Other key findings from the study include the following:
Exploits of Adobe Flash vulnerabilities are increasing. They are regularly integrated into widely used exploit kits such as Angler and Nuclear. Angler continues to lead the exploit kit market in terms of overall sophistication and effectiveness. The Angler Exploit Kit represents the types of common threats that will challenge organizations as the digital economy and the Internet of Everything (IoE) create new attack vectors and monetization opportunities for adversaries.
Operators of crime ware, like ransomware, are hiring and funding professional development teams to help them make sure their tactics remain profitable.
Criminals are turning to the anonymous web network Tor and the Invisible Internet Project (I2P) to relay command-and-control communications while evading detection.
Adversaries are once again using Microsoft Office macros to deliver malware. It’s an old tactic that fell out of favor, but it’s being taken up again as malicious actors seek new ways to thwart security protections.
Some exploit kit authors are incorporating text from Jane Austen’s classic novel Sense and Sensibility into web landing pages that host their exploit kits. Antivirus and other security solutions are more likely to categorize these pages as legitimate after “reading” such text.
Malware authors are increasing their use of techniques such as sandbox detection to conceal their presence on networks.
Spam volume is increasing in the United States, China, and the Russian Federation, but remained relatively stable in other regions in the first five months of 2015.
The security industry is paying more attention to mitigating vulnerabilities in open-source solutions.
Continuing a trend covered in the Cisco 2015 Annual Security Report, exploits involving Java have been on the decline in the first half of 2015.
A Call to Action:
The innovation race between adversaries and security vendors is accelerating, placing end users and organizations at increasing risk. Vendors must be vigilant in developing integrated security solutions that help organizations be proactive and align the right people, processes, and technology.
Integrated Threat Defense - Organizations face significant challenges with point product solutions and need to consider an integrated threat defense architecture that embeds security everywhere, and will enforce at any control point.
Services Fill the Gap - As the security industry addresses increased fragmentation, a dynamic threat landscape, and how to cope with a rising shortfall of skilled talent, businesses must invest in effective, sustainable and trusted security solutions and professional services.
Global Cyber Governance Framework - Global cyber governance is not prepared to handle the emerging threat landscape or geopolitical challenges. The question of boundaries — how governments collect data about citizens and businesses and share among jurisdictions — is a significant hurdle to achieving cohesive cyber governance as worldwide cooperation is limited. A collaborative, multi-stakeholder cyber governance framework is required to sustain business innovation and economic growth on a global stage.
Trustworthy Vendors - Organizations should demand that their technology vendors are transparent about and able to demonstrate the security they build into their products in order to be considered trustworthy. These organizations must carry this understanding across all aspects of product development starting with the supply chain and through the deployed life of their products. They must ask vendors to contractually back up their claims and demand better security.
Executive Quote:
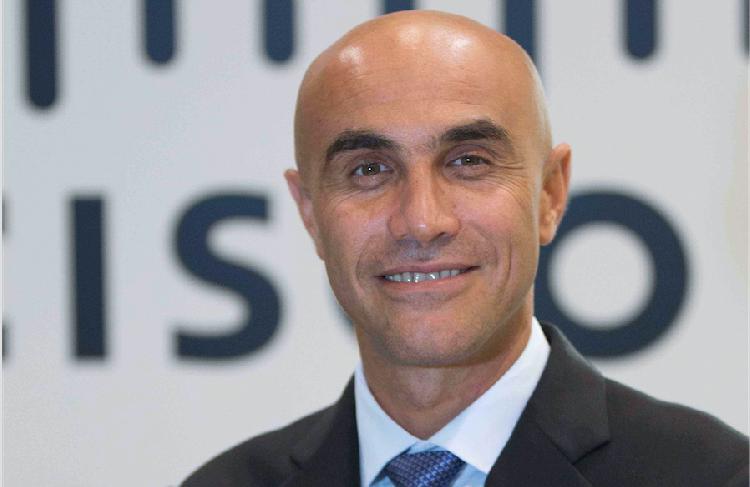
Rabih Dabboussi, General Manager, Cisco UAE:
“Organizations in UAE cannot just accept that compromise is inevitable, even if it feels like it today. The technology industry must up the game and provide reliable and resilient products and services, and the security industry must provide vastly improved, yet meaningfully simplified, capabilities for detecting, preventing, and recovering from attacks. This is where Cisco is leading. We are regularly told that business strategy and security strategy are the top two issues for our customers, and they want trusted partnerships with us. Trust is tightly linked to security, and transparency is key so industry-leading technology is only half the battle. We're committed to providing both: industry-defining security capabilities and trustworthy solutions across all product lines. The report findings also underscore the need for businesses to deploy integrated solutions vs. point products, work with trustworthy vendors, and enlist security services providers for guidance and assessment.”