Cisco 2018 Annual Cybersecurity Report Reveals Security Leaders Rely on and Invest in Automation
Malware sophistication is increasing as adversaries begin to weaponize cloud services and evade detection through encryption, used as a tool to conceal command-and-control activity. To reduce adversaries’ time to operate, security professionals said they will increasingly leverage and spend more on tools that use AI and machine learning, reported in the 11th Cisco® 2018 Annual Cybersecurity Report (ACR).
While encryption is meant to enhance security, the expanded volume of encrypted web traffic (50 percent as of October 2017) — both legitimate and malicious — has created more challenges for defenders trying to identify and monitor potential threats. Cisco threat researchers observed more than a threefold increase in encrypted network communication used by inspected malware samples over a 12-month period.
Applying machine learning can help enhance network security defenses and, over time, “learn” how to automatically detect unusual patterns in encrypted web traffic, cloud, and IoT environments. Some of the 3,600 chief information security officers (CISOs) interviewed for the Cisco 2018 Security Capabilities Benchmark Study report, stated they were reliant and eager to add tools like machine learning and AI, but were frustrated by the number of false positives such systems generate. While still in its infancy, machine learning and AI technologies over time will mature and learn what is “normal” activity in the network environments they are monitoring.
“Last year’s evolution of malware demonstrates that our adversaries continue to learn,” said John N. Stewart, Senior Vice President and Chief Security and Trust Officer, Cisco. “We have to raise the bar now – top down leadership, business led, technology investments, and practice effective security – there is too much risk, and it is up to us to reduce it.”
Cisco 2018 Annual Cybersecurity Report Additional Highlights
- The financial cost of attacks is no longer a hypothetical number:
- According to study respondents, more than half of all attacks resulted in financial damages of more than US$500,000, including, but not limited to, lost revenue, customers, opportunities, and out-of-pocket costs
- Supply chain attacks are increasing in velocity, complexity
These attacks can impact computers on a massive scale and can persist for months or even years. Defenders should be aware of the potential risk of using software or hardware from organizations that do not appear to have a responsible security posture.
- Two such attacks in 2017, Nyetya and Ccleaner, infected users by attacking trusted software.
- Defenders should review third-party efficacy testing of security technologies to help reduce the risk of supply chain attacks.
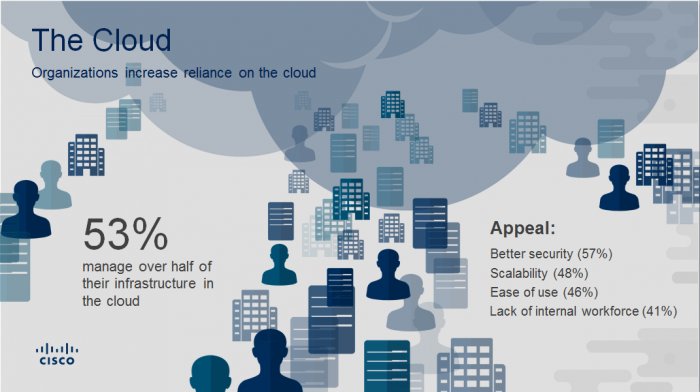
- Security is getting more complex, scope of breaches is expanding
Defenders are implementing a complex mix of products from a cross-section of vendors to protect against breaches. This complexity and growth in breaches has many downstream effects on an organization’s ability to defend against attacks, such as increased risk of losses.
- In 2017, 25 percent of security professionals said they used products from 11 to 20 vendors, compared with 18 percent of security professionals in 2016.
- Security professionals said 32 percent of breaches affected more than half of their systems, compared with 15 percent in 2016.
- Security professionals see value in behavioral analytics tools in locating malicious actors in networks
- 92 percent of security professionals said behavior analytics tools work well. Two-thirds of the healthcare sector, followed by financial services, found behavior analytics to work extremely well to identify malicious actors.
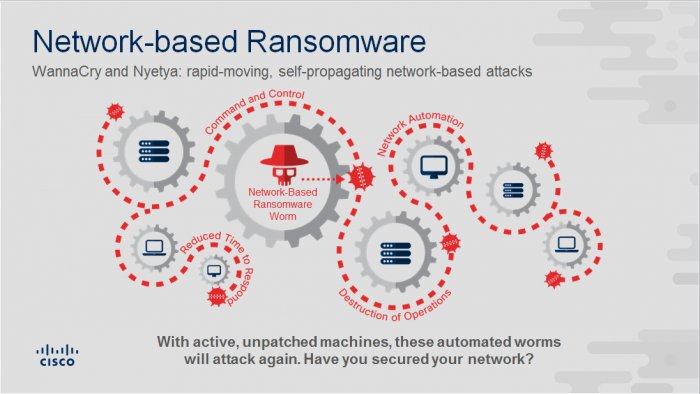
- Use of cloud is growing; attackers taking advantage of the lack of advanced security
- In this year’s study, 27 percent of security professionals said they are using off-premises private clouds, compared with 20 percent in 2016
- Among them, 57 percent said they host networks in the cloud because of better data security; 48 percent, because of scalability; and 46 percent, because of ease of use.
- While cloud offers better data security, attackers are taking advantage of the fact that security teams are having difficulty defending evolving and expanding cloud environments. The combination of best practices, advanced security technologies like machine learning, and first-line-of-defense tools like cloud security platforms can help protect this environment.
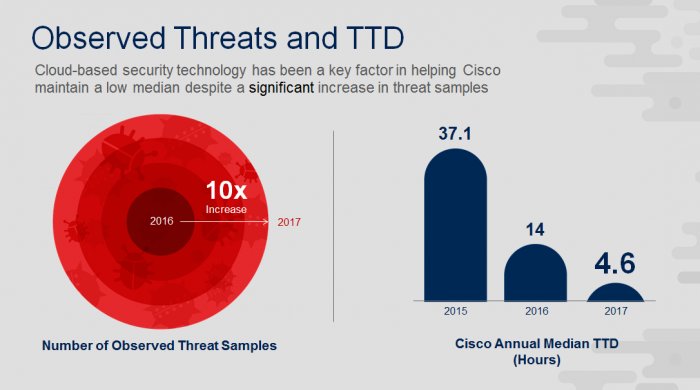
- Trends in malware volume have an impact on defenders’ time to detection (TTD)
- The Cisco median TTD of about 4.6 hours for the period from November 2016 to October 2017 — well below the 39-hour median TTD reported in November 2015, and the 14-hour median reported in the Cisco 2017 Annual Cybersecurity Report for the period from November 2015 to October 2016.
- The use of cloud-based security technology has been a key factor in helping Cisco to drive and keep its median TTD to a low level. Faster TTD helps defenders move sooner to resolving breaches.
Additional Recommendations for Defenders:
- Confirm that they adhere to corporate policies and practices for application, system, and appliance patching.
- Access timely, accurate threat intelligence data and processes that allow for that data to be incorporated into security monitoring.
- Perform deeper and more advanced analytics.
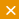
- Back up data often and test restoration procedures, processes that are critical in a world of fast-moving, network-based ransomware worms and destructive cyber weapons.
- Conduct security scanning of microservice, cloud service, and application administration systems.